Achalasia cardia is an uncommon condition affecting the esophagus where the lower esophageal valve fails to relax and normal propulsive movements of the esophagus are absent. As a consequence, individuals experience difficulty swallowing, the involuntary return of food (regurgitation), and discomfort in the chest area (chest pain). Long-term alleviation sometimes requires intervention.
Treatment Options
Based on the patient’s condition, Dr. Srikanth Gadiyaram, a highly trained gastrosurgeon, offers both surgical and non-surgical treatment options.
- Non-Surgical Option
- Pneumatic dilation:- It is a medical procedure known as pneumatic dilation that utilizes air pressure to expand a constricted passage or opening within the body.
- Botox: Recommended for individuals unable to undergo pneumatic dilation or surgery due to age or health conditions. Botox injections typically last six months or less. Botox improves achalasia diagnosis.
- Surgical treatment Options
- Heller Myotomy
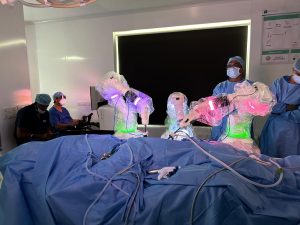
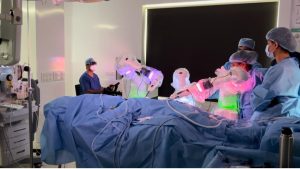
This is the gold standard treatment for achalasia cardia. The procedure involves division of the muscles at the lower esophageal sphincter to ease food passage into the stomach. Additionally, a valve is constructed using the upper stomach to prevent food from returning to the food pipe. Laparoscopic techniques involve small incisions, a camera, and specialized tools.
The hospital stay for a laparoscopic procedure is typically 24 hours. Patients typically recover fully within a few days and can resume normal activities.
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM)
It’s a less invasive alternative to Heller myotomy.
It involves creating an opening in the esophageal lining and cutting the inner circular muscle fibers of the lower esophageal sphincter. An endoscope is used in the procedure, eliminating the need for external incisions.
Patients usually recover quickly and can resume regular activities within a few days. The downside of this endoscopic procedure is post procedure reflux. Also, the experience with this procedure is limited to a few centers, and long-term results are lacking.
- Esophagectomy
It excites a portion or whole of the esophagus.
It is done on people with advanced achalasia who have a large esophagus and haven’t improved with other treatments. The stomach may be surgically repositioned to replace the esophagus, or a segment of the intestine may be used instead.
Effectively alleviate symptoms in severe cases. However, it has higher rates of illness and mortality compared to other approaches.
Recovery from an illness or injury can take several months. Post-treatment monitoring is necessary to address patients’ issues and meet their nutritional needs.
Dr. Srikanth Gadiyaram and his team carefully design peri-operative care regimens to maximize surgical success while improving patients’ outcomes.
Postoperative Care and Management
For a full recovery and lasting results, postoperative care is critical.
- Dietary modifications involve initiating a liquid diet, gradually transitioning to soft foods, and adopting a regular diet. It is advisable to consume small, frequent meals.
- Medications:- PPIs are commonly prescribed to address postoperative symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Regular monitoring is crucial for assessing esophageal function, identifying potential complications, and ensuring adequate nutritional intake.
Get in touch with us if you’re experiencing such symptoms and would like to evaluate your treatment options at 98801 05829.