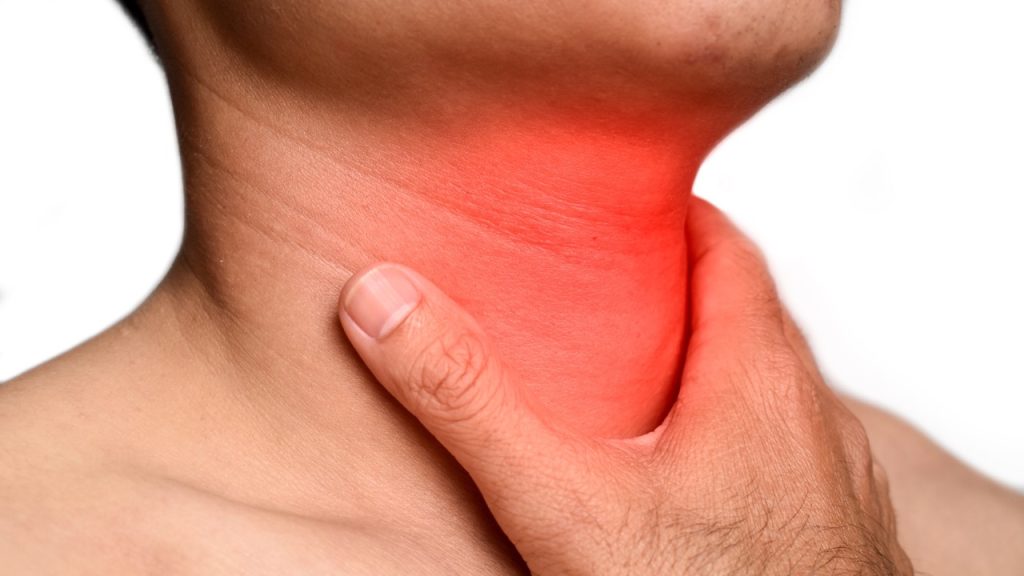
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. The proper function of the brain, nerves, muscles, valves, and esophagus is crucial for swallowing..
Common symptoms of dysphagia may include:
- Discomfort and difficulty while swallowing.
- Feeling food stuck in the throat, chest, or behind the breastbone.
- Excessive Salivating.
- Vocal cord strain
- Regurgitation or food reflux.
- Heartburn.
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Losing weight.
- Coughing or gagging during the act of swallowing.
Different forms of dysphagia
Swallowing difficulty can be categorized into two groups: oropharyngeal, which encompasses the initial three phases, and esophageal.
- Oropharyngeal Dysphagia:
The pharynx transports chewed food to the esophagus. Dysphagia causes food to stick to the throat. Some symptoms include pulmonary aspiration. Oesophageal dysphagia is caused by sphincter dysfunction.
- Esophageal dysphagia
It is characterized by impaired movement of solid or liquid substances through the esophagus, particularly in the area between the upper and lower esophageal sphincter. It occurs because of either aberrant movement of this part of the esophagus or actual obstruction to passage.
- Esophagogastric dysphagia
It is a condition where there is a problem with the movement of material from the lower esophageal sphincter to the gastric fundus, either owing to a motor issue or a physical blockage.
- Paraesophageal dysphagia
Occurs when there is infiltration or physical impingement on the wall and lumen of the esophagus. If this is prevalent, it could lead to motor complications in the esophagus.
Treatment approaches
Dr. Srikanth Gadiyaram, our acclaimed gastro surgeon, offers individualized treatment plans for dysphagia.
- Non- Surgical Procedure
- Speech and language therapists guide swallowing therapy. Exercise improves muscle strength and responsiveness.
- Dietary changes: Some foods and liquids are easier to eat. A balanced diet is crucial for easily digestible foods.
- Feeding through a nasal tube or PEG may be necessary for at-risk patients. PEG tubes are inserted into the stomach through an abdominal incision.
- Esophageal dilation uses a small balloon to widen the esophagus for stricture treatment. The balloon is placed, inflated, and eventually removed.
- Medical procedure.Pharmaceuticals.It involves prescription medications to decrease stomach acid levels. Continue taking these medications for a long time.
i) Corticosteroids may treat eosinophilic esophagitis. Smooth muscle relaxants help treat esophageal spasms.
ii) Nutrition. Your healthcare provider may recommend a specific dietary plan to alleviate your dysphagia symptoms. Diet changes may help treat eosinophilic esophagitis.
Minimally Invasive Modalities to Manage Dysphagia
- Laparoscopic cardiomyotomy with partial antireflux procedure is currently the established gold standard for managing dysphagia in Achalasia cardia.
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM)is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure to manage Achalasia cardia
- Stent Placement:- A stent can keep an obstructed or constricted esophagus open. Some stents are permanent for esophageal cancer patients, while others are removable.
- Botox/ OnabotulinumtoxinA:- It is usually administered into the esophageal sphincter muscle. It relaxes and improves swallowing in people with achalasia. This technique may require multiple injections, but it is less invasive than surgery.
Make an appointment at Sahasra Hospital by calling 9880105829 if you are concerned and want more information about the surgery or treatment plans